Lyophilization technology has gained widespread adoption due to its ability to retain the original properties of the material, such as flavor, aroma, and bioactivity, while extending its shelf life. It finds applications in pharmaceuticals, food, biotechnology, and other sectors where preservation is crucial.
What is Lyophilization Technology?
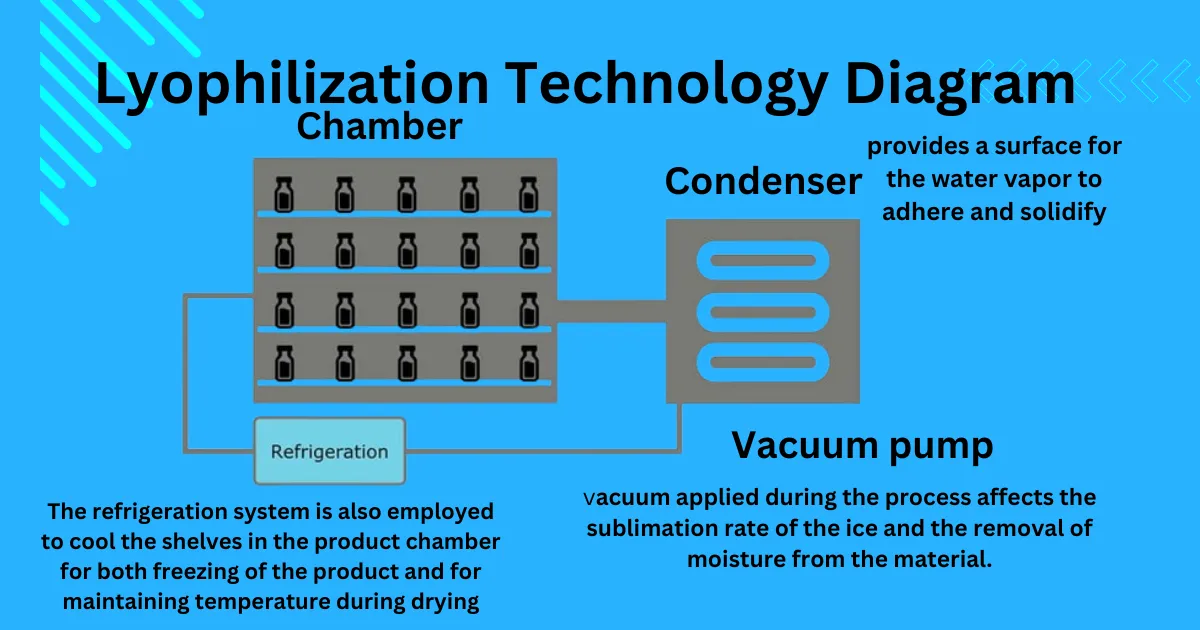
Lyophilization technology, also known as freeze-drying, is a process used in various industries to preserve perishable materials by removing the moisture content from them. This technique involves freezing the material and then subjecting it to a vacuum, which allows the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor, leaving behind a dried product.
Understanding the Lyophilization Process
Importance of Lyophilization
Lyophilization is vital for preserving heat-sensitive materials that may degrade under high temperatures. By removing moisture at low temperatures, it helps maintain the integrity of the product.
Steps involved in Lyophilization
Usually, there are three main steps in the lyophilization process: Loading stage, freezing, primary drying, secondary drying. and stoppering stage, Freezing solidifies the material, primary drying removes the majority of the water, and secondary drying removes any remaining moisture to achieve the desired dryness level.
Loading stage: After starting the freeze freeze dryer then loading temperature achived then open the freeze dryer door in aseptic area side and loading the empty and filled vial in freeze dryer and then start the freezing Cycle by SCADA or
Loading stage: Once the freeze dryer is started and the loading temperature is reached, the door is opened in a sterile area. Empty and filled vials are then loaded into the freeze dryer before initiating the freezing cycle using SCADA.
Freezing: A material changes from a liquid to a solid state during freezing. This transition occurs when the liquid’s molecules slow down enough to be arranged into a solid form with definite places by their attraction forces.
Primary Drying (Sublimation): Pressure is lowered, and heat is added to allow the ice to sublimate directly into vapor. During the primary drying phase, water vapor adheres to and solidifies on the cold condenser surface, protecting the vacuum pump from moisture. Approximately 95% of the material’s water content is removed during this slow process.
Secondary Drying (Desorption): Remaining moisture is removed by further lowering pressure and raising temperature. or Water desorption from the cake starts in the same spot as primary freeze-drying is finished and all ice has been removed via sublimation. The primary drying phase is when this stage, called secondary drying, begins.
Stoppering stage: After completing the secondary drying process, vials are fully stoppered in the freeze dryer using the stoppering force applied by the shelf.
Applications of Lyophilization Technology
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, lyophilization is used to stabilize drugs, vaccines, and other biological products. It allows for long-term storage without the need for refrigeration and helps maintain the potency of the medications. Here are some applications of lyophilization technology:
- Pharmaceuticals: Lyophilization is extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry to preserve and stabilize drugs, vaccines, and biological products. It allows for long-term storage without the need for refrigeration and helps maintain the potency and efficacy of medications.
- Diagnostic Kits: Lyophilization is used to produce stable reagents and components for diagnostic kits used in medical diagnostics and research laboratories. Lyophilized reagents offer extended shelf life and improved stability, facilitating accurate and reliable test results.
- Cosmetics: Lyophilization is employed in the cosmetics industry to preserve the active ingredients in skincare products, such as serums, creams, and masks. By removing moisture from the formulations, lyophilization helps maintain the efficacy and stability of the products, ensuring consistent performance over time.
- Veterinary Medicine: Lyophilization is used in the production of veterinary vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and diagnostic reagents. It ensures the stability and potency of veterinary products, allowing for convenient storage and transportation under varying environmental conditions.
- Food Industry: In the food industry, lyophilization is employed to preserve perishable foods such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. It retains the nutritional value and sensory characteristics of the food while extending its shelf life.
- Biotechnology: In biotechnology, lyophilization is utilized for the preservation of enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It enables the long-term storage of biological samples and reagents without compromising their functionality.
Advantages of Lyophilization
Lyophilization offers several advantages over other drying methods, including:
- Preservation of product quality
- Extended shelf life
- Reduced weight and volume
- Enhanced stability during storage and transportation
Challenges in Lyophilization
Despite its benefits, lyophilization presents challenges such as high production costs, long processing times, and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
Factors Affecting Lyophilization Process
Several factors can influence the efficiency of the lyophilization process, including the composition of the material, freezing rate, vacuum level, and drying temperature. Here are ten factors that can affect the lyophilization process:
- Composition of the Material: The composition of the material being lyophilized, including its chemical structure, viscosity, and presence of additives, can impact the process efficiency.
- Freezing Rate: The rate at which the material is frozen can affect the formation of ice crystals, which in turn influences the drying kinetics and the final product’s quality.
- Vacuum Level: The level of vacuum applied during the process affects the sublimation rate of the ice and the removal of moisture from the material. Optimal vacuum conditions are crucial for efficient drying.
- Drying Temperature: The temperature at which the drying phase occurs plays a significant role in determining the rate of sublimation and the preservation of product integrity.
- Product Container Design: The design and material of the container holding the material being lyophilized can impact heat transfer, product collapse, and drying uniformity.
- Pre-treatment of the Material: Pre-treating the material before lyophilization, such as pre-freezing or adding cryoprotectants, can influence ice crystal formation and product stability.
- Shelf Configuration: The arrangement of shelves within the lyophilizer affects the heat and mass transfer dynamics, as well as the uniformity of drying across the product.
- Process Parameters Control: Monitoring and controlling parameters such as pressure, temperature, and shelf movement throughout the lyophilization cycle are critical for consistent and reproducible results.
Equipment Used in Lyophilization
The equipment used in lyophilization includes freeze dryers, which consist of a chamber for holding the product, shelves for loading trays, and vacuum pumps for creating the necessary vacuum.
Lyophilization vs. Other Drying Methods
Compared to other drying methods such as air drying and spray drying, lyophilization offers superior preservation of product quality but may be more expensive and time-consuming.
Future Trends in Lyophilization Technology
Advancements in lyophilization technology are focused on improving process efficiency. reducing costs and expanding applications in emerging fields such as personalized medicine and regenerative therapy.
Safety Considerations in Lyophilization
Safety considerations in lyophilization include proper handling of cryogenic materials, prevention of contamination, and adherence to regulatory guidelines for product safety. Here are some safety considerations in lyophilization:
- Cryogenic Material Handling: Follow proper safety protocols to prevent exposure to extreme cold temperatures and potential hazards associated with handling cryogenic substances.
- Equipment Safety: Ensure that lyophilization equipment is properly maintained. and follows the safety precautions and instructions provided by the manufacturer. Regular inspections and maintenance routines should be in place to mitigate the risks of equipment malfunctions or accidents.
- Contamination Prevention: Implement strict cleanliness and contamination control measures throughout the lyophilization process to prevent microbial contamination or cross-contamination between batches. Proper cleaning and sterilization of equipment, as well as adherence to aseptic techniques, are essential for maintaining product safety.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and lab coats, to personnel involved in the lyophilization process. PPE helps protect workers from exposure to hazardous materials and ensures their safety while handling chemicals or operating machinery.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop and communicate emergency procedures for dealing with accidents or incidents that may occur during lyophilization operations. Such as spills, equipment failures, or chemical exposures. Training employees on emergency response protocols and providing access to emergency response equipment, such as eyewash stations or spill kits, is crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring swift response to emergencies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to regulatory guidelines and standards established by organizations such as the FDA or EMA for the safe production and handling of lyophilized products. Compliance with regulatory requirements ensures safety protocols.
Environmental Impact of Lyophilization
While lyophilization can reduce food waste by extending the shelf life of perishable foods, it also consumes energy and resources, contributing to environmental concerns. Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable lyophilization processes.
Case Studies on Lyophilization Success
Several case studies demonstrate the successful application of lyophilization technology in various industries, highlighting its effectiveness in preserving sensitive materials and improving product stability.
Regulatory Guidelines for Lyophilization
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA provide guidelines for the development, validation, and production of lyophilized products to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality. Here are some regulatory guidelines for lyophilization:
- Process Validation: Establish a robust process validation plan that includes the determination of critical process parameters (CPPs). And critical quality attributes (CQAs) related to lyophilization.
- Aseptic Processing: Implement stringent aseptic processing techniques during lyophilization to minimize the risk of microbial contamination and ensure product sterility.
- Analytical Methods Validation: Validate analytical methods used for in-process testing and release testing. And stability testing of lyophilized products to ensure accurate and reliable results.
- Lyophilization Cycle Development: Develop lyophilization cycles that are based on scientific principles. And tailored to the specific characteristics of the product. Considering factors such as formulation, container size, and drying kinetics.
- Cleaning and Sanitization Procedures: Establish validated cleaning and sanitization procedures for lyophilization equipment. And facilities to prevent cross-contamination and maintain product purity.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintain comprehensive documentation of all lyophilization activities. Including batch records, process deviations, and validation reports, in accordance with regulatory requirements for traceability and accountability.
Conclusion: The Future of Lyophilization Technology
Lyophilization technology plays a crucial role in preserving and stabilizing a wide range of materials in pharmaceuticals, food, and biotechnology. Despite its challenges, ongoing advancements are expected to further enhance efficiency. And affordability and sustainability of lyophilization processes.
Unique FAQs
Is lyophilization the same as freeze-drying?
While lyophilization and freeze-drying are often used interchangeably,. Lyophilization specifically refers to the process of removing water from a frozen material through sublimation.
How does lyophilization contribute to food preservation?
By removing moisture from food products, lyophilization inhibits the growth of microorganisms. And enzymes that cause spoilage, extending the shelf life of perishable foods.