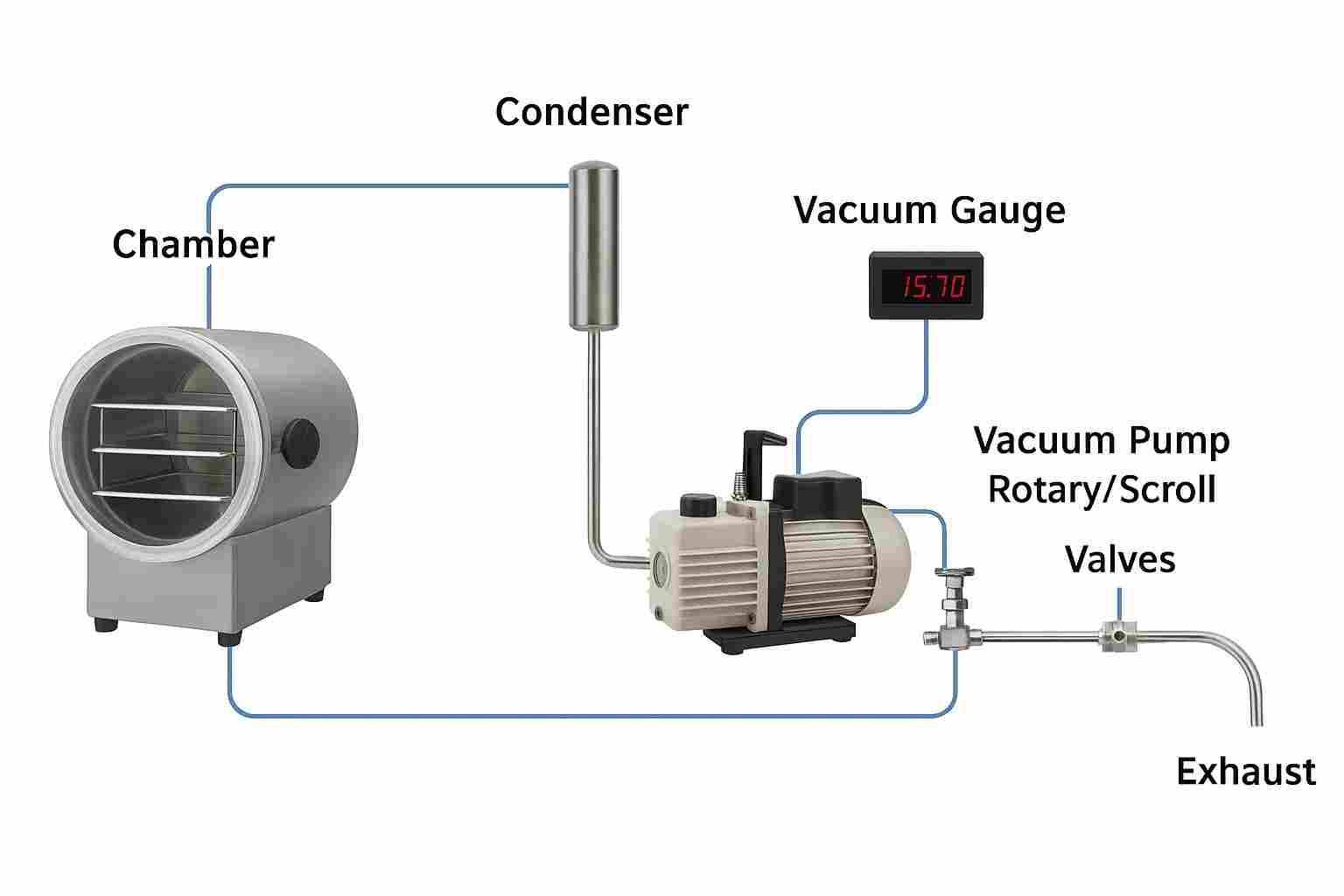
The lyophilizer vacuum pump is one of the most critical components in the freeze-drying process, ensuring low pressure for efficient sublimation. Together with the condenser, Pirani gauge, and nitrogen venting system, it creates a controlled environment that supports faster drying, prevents product melting, and improves reliability. A clear understanding of how each part functions helps operators optimize performance, maintain product quality, and reduce downtime during lyophilization
In this article, we delve into the world of lyophilizer vacuum pumps, exploring their functionality, types, applications, maintenance tips, and much more.
What is a Lyophilizer Vacuum Pump?
A lyophilizer vacuum pump is its primary function in the lyophilization process. In the realm of industrial processes like freeze-drying, efficiency and reliability are paramount. One critical component that ensures the success of freeze-drying processes is the lyophilizer vacuum pump.
- Low ultimate pressure and high pumping speed
- Pressure in the fine vacuum range, well below 1 mbar, is usually required for sublimation
- Rapid reduction of pressure to the target pressure is essential to prevent samples from melting
- high pumping speed of the vacuum pump is important for efficient sublimation
- Residual drying requires the lowest possible ultimate vacuum in the range of 10–3 mbar
- Use of corrosion-resistant vacuum pumps, such as the chemistry screw pump or the chemistry-HYBRID pump, is recommended when solvents are used.
How does a Lyophilizer Vacuum Pump work?
These pumps operate on the principle of creating a vacuum by removing air and other gases from the lyophilization chamber. This vacuum lowers the boiling point of water, allowing it to transition directly from a solid to a vapor state without passing through the liquid phase, thereby preserving the integrity of the product.
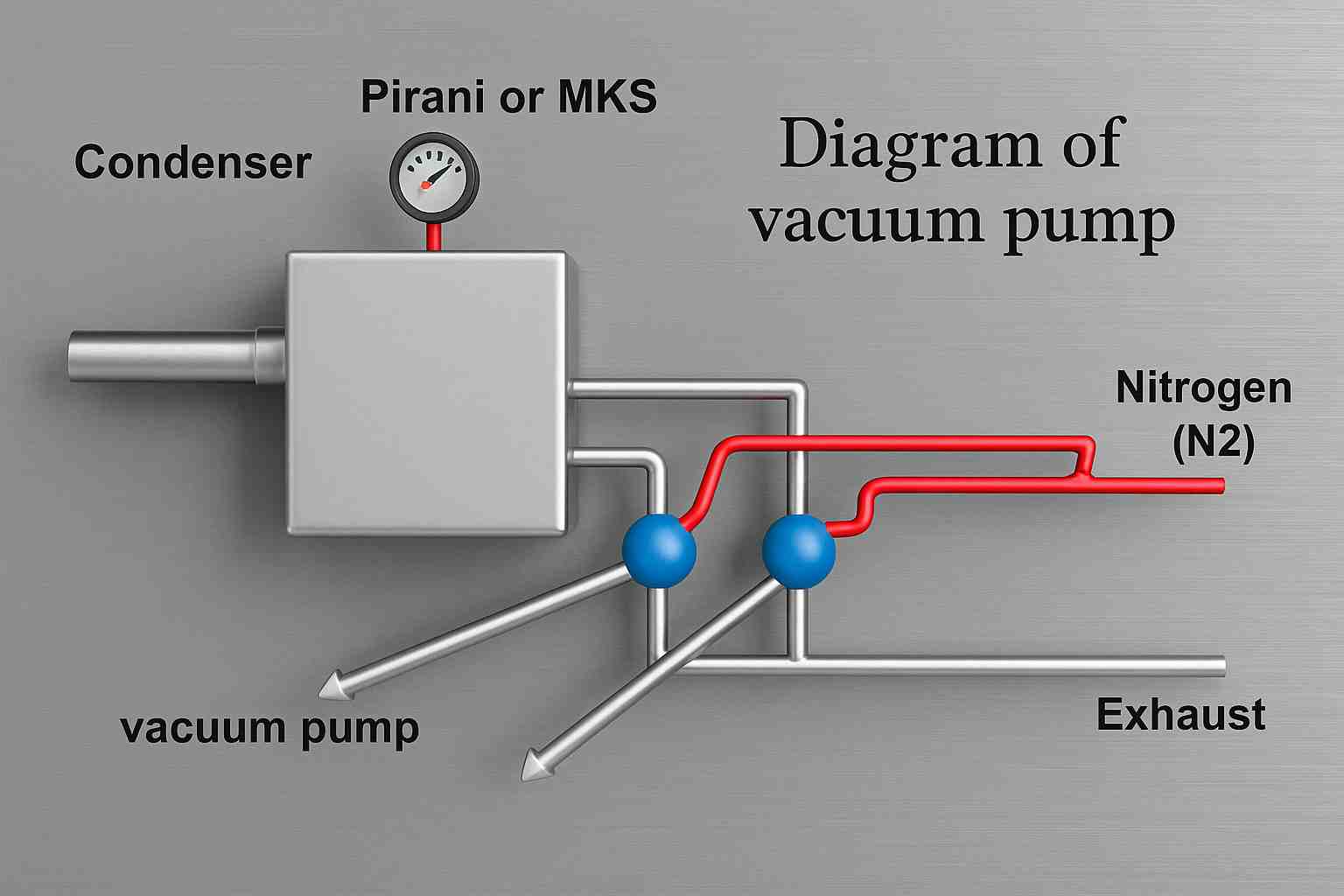
Schematic diagram of vacuum pump
Condenser
The condenser collects the vapor (like water vapor or solvent vapor) that comes out during the vacuum process. It cools the vapor so it turns into liquid and gets trapped, preventing it from entering the vacuum pump.
Condenser → traps vapor so it doesn’t reach the pump The condenser is a vital part of the system, as it traps vapors before they can reach the vacuum pump. By converting vapor into ice, it prevents contamination and improves pump life.
Pirani or MKS Gauge
This is a vacuum gauge that measures the pressure inside the system. Pirani gauge is used for low and medium vacuum ranges, while MKS gauge is used for more precise and wide vacuum ranges. And it helps operators monitor how deep the vacuum is.
Pirani/MKS gauge → measures vacuum pressure. Accurate vacuum monitoring is achieved using sensors like the Pirani gauge or MKS gauge. These instruments help maintain the correct pressure during both primary and secondary drying stages.
Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump removes air and gases from the system. By creating a vacuum, it allows sublimation (solid turning to vapor directly), which is very important in freeze-drying (lyophilization) and other vacuum processes.
Vacuum pump → removes air/gases to create vacuum.
Nitrogen (N₂) Line Purging and Venting
Nitrogen gas is used for nitrogen venting/purging the system. It prevents contamination, keeps the system clean, and is often used before breaking the vacuum (venting). It ensures that no oxygen or moisture enters when the system is opened.
Nitrogen line (N₂) → used for purging/venting safely. prevents oxidation, contamination, and moisture ingress when breaking the vacuum
Valves (Blue Circles in Image)
These control the flow of gases (vacuum and nitrogen). One valve directs air towards the vacuum pump, and the other allows nitrogen into the chamber. Proper operation of these valves ensures smooth vacuum control.
Valves → control gas flow between pump, nitrogen, and chamber
Exhaust
The exhaust is where the removed gases are released from the pump. It ensures safe disposal of gases from the system.
Exhaust → releases gases from the pump. The system creates vacuum, traps vapors, measures pressure, purges with nitrogen, and safely exhausts gases.
👍 Here’s a simple comparison table
- Failure of the vacuum pump: The failure of the vacuum pump appears when the motor cantactor is switched on but the massege is not given.
- Motor Contactor Failure: This occurs when the motor contactor is switched on but the “ON” signal is not given, indicating a possible electrical issue.
The cause of this failure due to following reasion:
- Motor Protection Switch: One of the motor protection switches has been cut out and switched off the corresponding vacuum pump.
- The failure of the vacuum pump is indicated by the monitoring system’s guard alert.
- Failure of oil temperature: The oil temperature has exceeded the warning limit. it could lead to pump failure.
- Failure level: The oil level dropped below minimum or A pump failure can occur if the oil level drops below the minimum requirement.
- Failure vibration: the vibration level has exceeded the warning limit. or High vibration levels beyond the warning limit may indicate impending pump failure.
- Failure exhaust pressure: The exhaust pressure exceeds the maximum permissible pressure of 11000 to 1200 Mbar. If the exhaust pressure surpasses the maximum permissible limit of 1100 to 1200 mbar, it can lead to pump failure.
Summary: Vacuum pump failure in a lyophilizer can result from various factors such as electrical issues, tripped motor protection switches, monitoring system alerts, oil temperature or level problems, excessive vibration, or exceeding exhaust pressure limits. Troubleshooting involves checking connections, resetting switches, monitoring oil conditions, and adjusting parameters to resolve the issue promptly.
Types of Lyophilizer Vacuum Pumps
Here are different types of vacuum pumps commonly used in lyophilization processes, such as oil-sealed rotary vane vacuum pumps, scroll vacuum pumps, and diaphragm vacuum pumps.
Advantages of Lyophilizer Vacuum Pumps
Lyophilizer vacuum pumps offer numerous benefits, including high efficiency, robustness, and scalability. Their ability to maintain precise vacuum levels and handle various solvents makes them invaluable assets in freeze-drying processes.
- Fast Sublimation Rates: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps facilitate rapid sublimation rates by creating the necessary vacuum environment, speeding up the freeze-drying process.
- Versatility: They can accommodate a wide range of products and formulations, from pharmaceuticals to food and biological samples.
- Reliability: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps are known for their reliability and robustness, ensuring consistent performance even in demanding industrial environments.
- Low Maintenance: Many lyophilizer vacuum pumps require minimal maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Scalability: They are available in various sizes and capacities, making them suitable for both laboratory-scale research and large-scale industrial production.
- Compact Design: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps often feature a compact design, saving valuable space in manufacturing facilities and laboratories.
- Energy Efficiency: Some modern vacuum pumps are designed for energy efficiency, reducing power consumption and operating costs.
- Compatibility: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps are compatible with a range of lyophilization equipment and processes, providing seamless integration and reliable performance.
Applications of Lyophilizer Vacuum Pumps
These vacuum pumps find applications across diverse industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and biotechnology. From preserving sensitive pharmaceutical formulations to enhancing the shelf life of food products, lyophilizer vacuum pumps play a crucial role in ensuring product quality and stability. Here are some important points related to the applications of Lyophilizer Vacuum Pumps.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps are extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry for the freeze-drying of medications, vaccines, and biological products, preserving their stability and efficacy.
- Food Preservation: They play a crucial role in the food industry for preserving perishable food items such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products by removing moisture and extending their shelf life.
- Biotechnology: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps are vital in biotechnology for the preservation of enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules, maintaining their activity and stability during storage and transportation.
- Research and Development: They are indispensable tools in research laboratories for studying the effects of freeze-drying on various materials, facilitating experiments, and optimizing processes.
- Chemical and Material Sciences: Lyophilizer vacuum pumps find applications in chemical and material sciences for drying and preserving sensitive compounds, polymers, and advanced materials, ensuring their quality and integrity.
Maintenance and Care Tips for Lyophilizer Vacuum Pumps
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the smooth operation and longevity of lyophilizer vacuum pumps. Simple tasks such as lubrication, filter replacement, and system inspection can significantly extend the lifespan of these critical components.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Failure of the vacuum pump: Despite their reliability, lyophilizer vacuum pumps may encounter issues such as oil contamination or pump failure. Understanding common problems and implementing timely troubleshooting measures is key to minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Vacuum systems may face operational challenges such as leaks, pressure fluctuations, or low pumping speed. A proper system leak test helps detect leakage sources and ensures efficient operation.
Future Trends in Lyophilizer Vacuum Pump Technology
The future of lyophilizer vacuum pumps lies in innovation and technological advancement. From energy-efficient designs to automation and remote monitoring capabilities, manufacturers are constantly striving to enhance the performance and sustainability of these essential devices.
Conclusion
The lyophilizer vacuum pump is an essential component in industrial freeze-drying, responsible for maintaining the low pressure needed for efficient sublimation and moisture removal. Along with key parts such as the condenser, Pirani gauge, and nitrogen venting system, it ensures precise vacuum control, product stability, and consistent results across various industries. Regular maintenance, leak testing, and the use of corrosion-resistant pumps are crucial for optimal performance and long service life. As technology advances, future trends in lyophilizer vacuum pumps will emphasize greater energy efficiency, sustainability, and enhanced reliability. Overall, these pumps play a vital role in achieving high-quality outcomes in modern industrial processes.
FAQs
What is the vacuum required for lyophilization?
The vacuum required for lyophilization typically ranges from below 1 mbar for sublimation to around 10–3 mbar for residual drying.
What is the difference between a speed vacuum and a lyophilizer?
The main difference between a speed vacuum and a lyophilizer is the mechanism of moisture removal. A speed vacuum uses centrifugal force to evaporate solvents rapidly, while a lyophilizer employs freeze-drying, which involves freezing the sample and then removing the ice by sublimation under vacuum.
What are the two types of vacuum pumps?
The two main types of vacuum pumps commonly used in lyophilization processes are oil-sealed rotary vane vacuum pumps and diaphragm vacuum pumps.
What are some common causes of vacuum pump failure in a lyophilizer?
Some common causes include motor contactor failure, motor protection switch tripping, high oil temperature, low oil level, excessive vibration, and exceeding exhaust pressure limits.
What is motor contactor failure, and how does it manifest in a vacuum pump?
Motor contactor failure occurs when the motor contactor is switched on. But it does not receive the “ON” signal, indicating a possible electrical issue.
What are the consequences of exceeding the warning limit for oil temperature in a vacuum pump?
Exceeding the warning limit for oil temperature can lead to pump failure, compromising the lyophilization process.
What is the significance of maintaining the oil level in a vacuum pump?
Maintaining the oil level above the minimum requirement is crucial, as a drop below this level can result in pump failure, disrupting the lyophilization process.