Dose variation in freeze-dried pharmaceuticals is a critical issue in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly in lyophilization (freeze-drying) processes. Maintaining dose uniformity is essential for ensuring product quality, safety, and efficacy.
However, inconsistencies during freeze-drying often lead to this variation, which can compromise drug potency, regulatory compliance, and patient outcomes.
By understanding the causes, risks, detection methods, and solutions, manufacturers can significantly improve the reliability of their lyophilization processes.
What is Dose Variation in Freeze-Dried Pharmaceuticals?
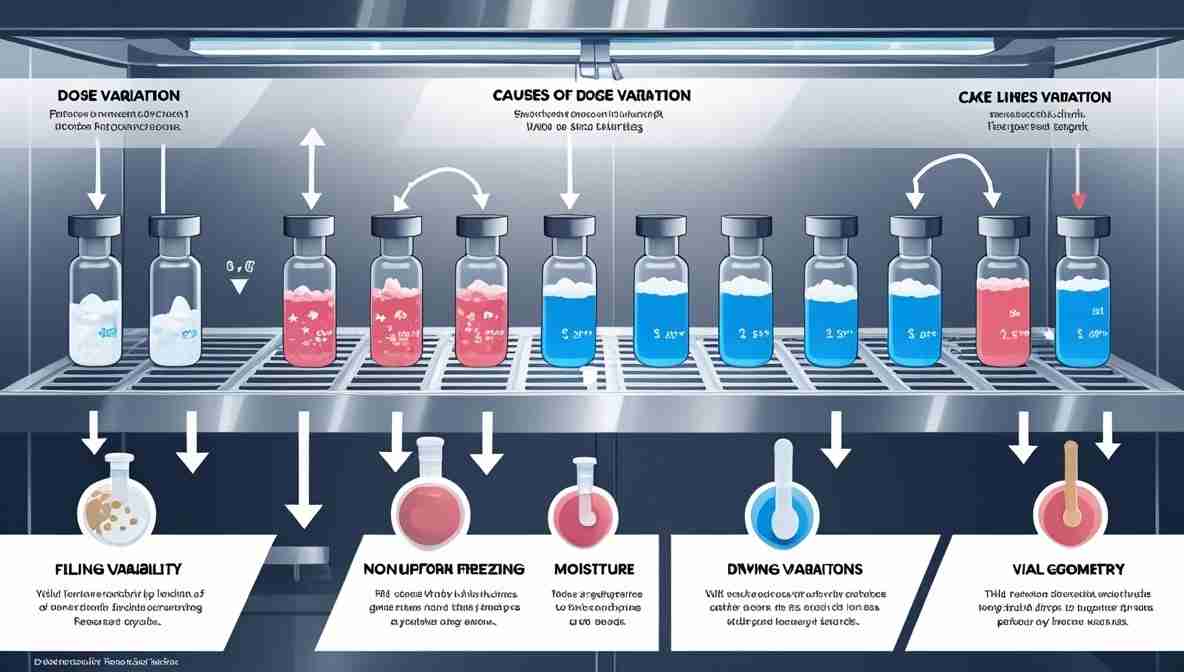
Dose variation refers to differences in the actual content or appearance of the lyophilized drug product across different vials or containers, despite having similar initial fill volumes. In freeze-dried pharmaceuticals, this can be visually assessed by the height or volume of the dried cake within a container.

Two key types of dose variation include
- High dose: Product volume significantly above the level seen from outside of the containern compared with another container that iss having a similarill volume.
- Low dose (lack of volume): Product volume significantly below the level seen from outside of the containern compared with anotherontainer that iss having a similar fill volume.
Such inconsistencies can arise from various technical, mechanical, and procedural flaws, making dose variation a complex challenge to address.
Causes of Dose Variation in Freeze-Dried Products
Several factors contribute to dose variation during the lyophilization process:
Filling Variability:
Inaccurate filling machines can lead to unequal fill volumes, even when the system appears calibrated. And foaming or splashing during filling can also result in uneven drug distribution.
Non-uniform Freezing:
Uneven freezing rates can cause differences in ice structure and sublimation patterns, leading to inconsistencies in the final cake structure. And Improper shelf loading or cold spots on the shelf may cause one vial to freeze faster or more completely than another.
Primary and Secondary Drying Variations
Inconsistent shelf temperatures or vacuum levels can influence the drying rate across vials. Variations in heat transfer due to differences in vial contact or shelf flatness.
Product Formulation and Vial Geometry
Viscosity and solid content of the formulation can affect product flow and reconstitution properties. Minor differences in vial height, diameter, or glass quality can lead to variable heat transfer.
For more on related freeze-drying defects, you can explore Defects in Lyophilized Product: A Complete Easy Guide.
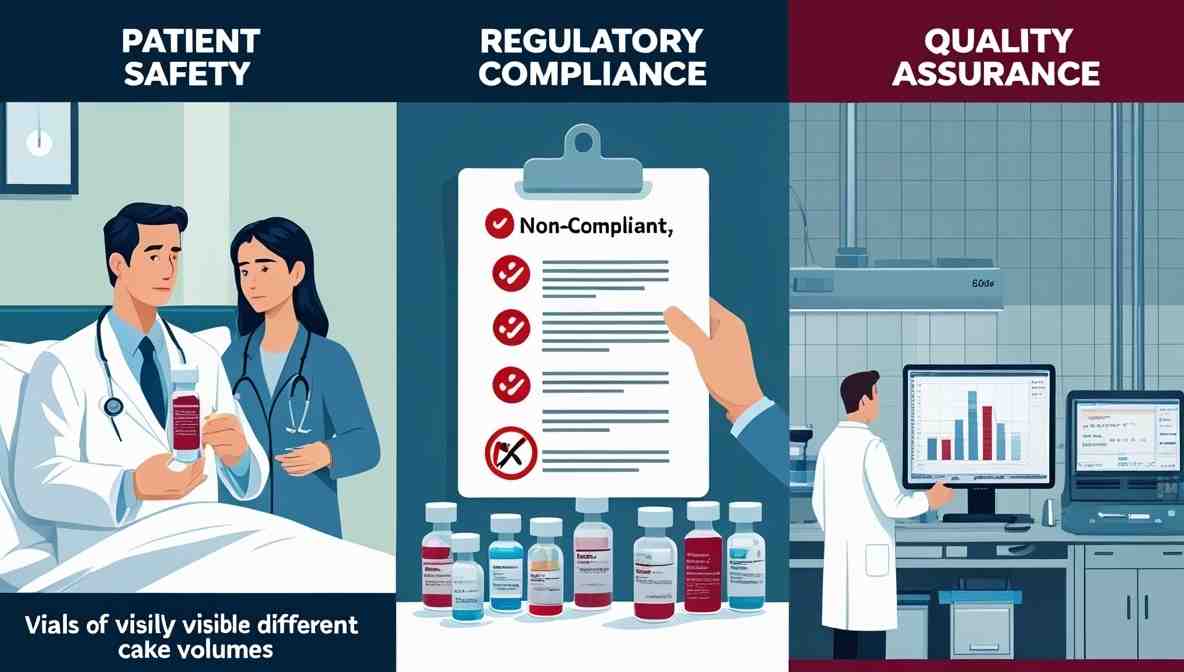
Impact of Dose Variation
Dose variation is not a mere visual issue; it poses critical pharmaceutical risks:
Patient Safety: An incorrect dose may lead to underdosing (ineffectiveness) or overdosing (toxicity).
Regulatory Compliance: Authorities like the FDA demand strict adherence to dosage specifications; deviations can lead to recalls or product rejection.
Quality Assurance: Variation may indicate underlying process problems, suggesting that the system is not under control.
A relevant internal resource is the Freeze Dryer Batch Inspection Checklist, which supports quality control teams in preventing such issues.
Detection of Dose Variation
Visual Inspection: Manual observation of cake height and structure across vials. and Common in routine production for early-stage detection.
Weight-Based Testing: Weighing the filled and lyophilized vials to ensure consistency.
Imaging Technology: Automated optical systems can detect cake collapse, shrinkage, or meltback, which are often associated with dose variation.
Analytical Testing: HPLC and other chemical assays to confirm active ingredient levels.
Refer to How to Identify Critical Defects in Lyophilized Pharmaceuticals for further guidance on defect detection.
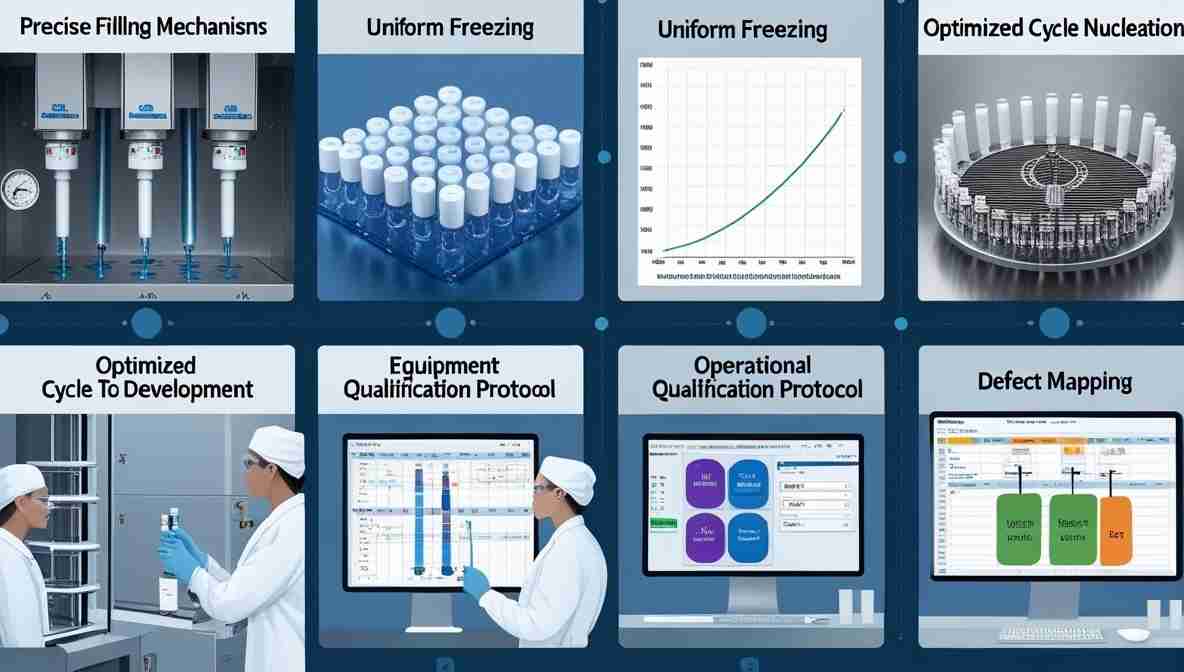
Solutions to Minimize Dose Variation
Precise Filling Mechanisms: Use high-precision pumps and regular calibration routines.
Uniform Freezing: Pre-cool shelves uniformly and ensure symmetric loading patterns. and Use controlled nucleation methods for better crystal uniformity.
Optimized Cycle Development: Proper primary and secondary drying parameters must be established based on product-specific thermal characteristics. and Refer to the Lyophilization Cycle Development Guide for Success to optimize freeze-drying cycles.
Equipment Qualification: Ensure shelves, condensers, and chamber vacuum are functioning per standards.
Implement Freeze Dryer Operational Qualification Protocol.
Defect Mapping: Monitor for related anomalies such as meltback, foreign matter, and fogging.
Read about Meltback Defect in Lyophilized Cake and Foreign Matter in Lyophilized Product.
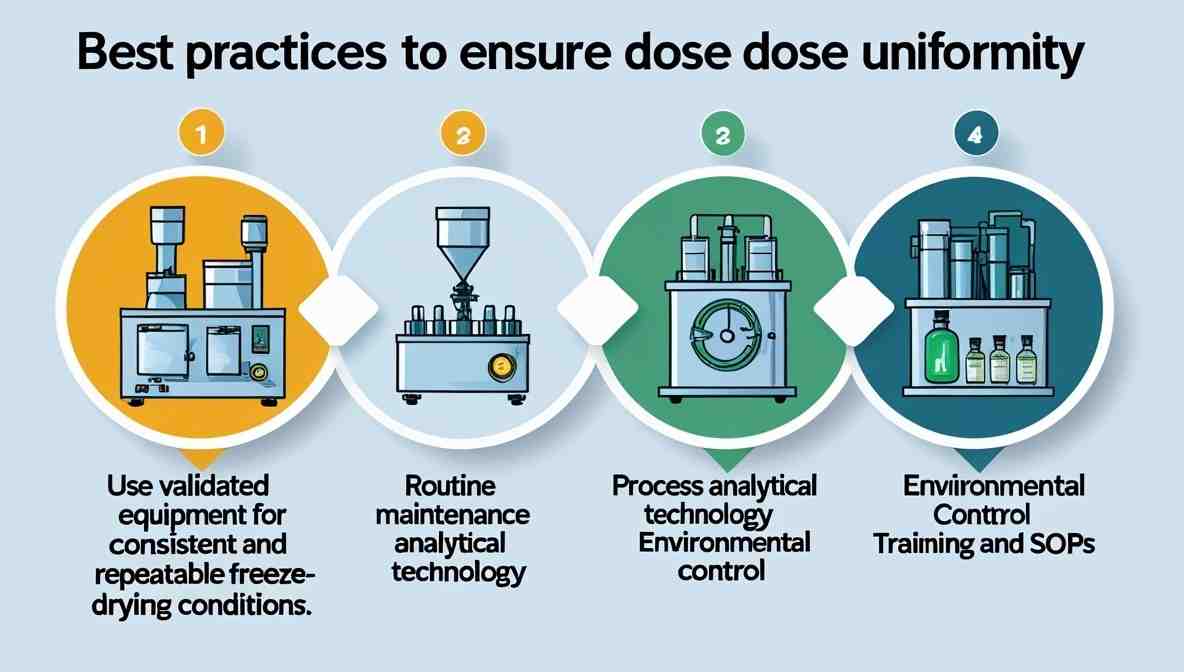
Best Practices to Ensure Dose Uniformity
Use validated equipment for consistent and repeatable freeze-drying conditions.
Routine maintenance of pumps, shelves, and sensors.
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) for real-time monitoring.
Environmental control: Maintain room temperature, humidity, and airflow per GMP standards.
Training and SOPs: Ensure all operators understand the criticality of uniform loading, filling, and handling procedures.
Explore the Pharmaceutical Freeze-Drying Q&A Guide for expert answers on best practices.
Case Insight: Preventing Dose Variation through Automation
A growing number of pharmaceutical companies are investing in automated freeze-drying systems that reduce human error and ensure tighter control of process parameters. These advanced systems incorporate
- Automated vial loading/unloading
- Real-time vacuum and temperature control
- Optical sensors to detect cake irregularities
For example, the adoption of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) has been instrumental in identifying the point at which sublimation is complete, thus preventing overdrying or underdrying—both of which could lead to dose inconsistencies.
For more on automation, refer to this informative article from Pharmaceutical Online on automated lyophilization systems.
Conclusion
Dose variation in freeze-dried pharmaceuticals remains one of the most critical challenges in ensuring drug quality and safety. From mechanical issues to formulation variability, multiple factors can disrupt dosage accuracy. However, with advanced technology, rigorous quality controls, and a deep understanding of freeze-drying mechanics, manufacturers can greatly reduce the risk of dose variation.
By integrating validated procedures, effective equipment qualification, and enhanced training protocols, the pharmaceutical industry can achieve consistency, compliance, and confidence in every freeze-dried vial.
For a deeper dive into related lyophilization topics, visit
- Lyophilized Product Quality Standards: A Comprehensive Guide
- Applications of Freeze-Drying in Biopharmaceuticals
- Dry Layer Resistance During Primary Drying
FAQs based on the article “Understanding Dose Variation in Freeze-Dried Pharmaceuticals
What is dose variation in freeze-dried pharmaceuticals?
Dose variation refers to inconsistencies in the amount or volume of the freeze-dried product across vials, despite similar fill volumes.
Why is dose uniformity important in lyophilized products?
Uniform dosing ensures patient safety, product efficacy, regulatory compliance, and consistent product quality.
What causes high or low dose appearance in lyophilized vials?
Common causes include inaccurate filling, non-uniform freezing, inconsistent drying parameters, and vial geometry differences.
How can high and low dose variations be visually identified?
High dose: Product volume appears significantly above other vials.
Low dose: Product volume appears significantly below other vials with the same fill.
Can meltback and cake shrinkage contribute to dose variation?
Yes, defects like meltback, collapse, or cake shrinkage can lead to perceived or actual dose variation.
(See related guide: Meltback Defect in Lyophilized Cake)
What techniques are used to detect dose variation?
Visual inspection, weight checks, optical imaging, and analytical methods such as HPLC are commonly used.
How does equipment qualification help reduce dose variation?
Proper qualification ensures consistent performance of freeze-drying shelves, vacuum systems, and temperature control components.
(Explore: Freeze Dryer Operational Qualification)
Can automation help eliminate dose variation issues?
Yes, automation improves filling precision, loading consistency, and real-time monitoring to reduce human error and enhance uniformity.
What role does freeze-drying cycle development play in dose control?
A well-designed lyophilization cycle ensures consistent drying behavior and helps avoid under- or overdrying that can impact dose appearance.
Are there GMP guidelines related to dose uniformity in freeze-dried products?
Yes, regulatory bodies like the FDA require strict dose uniformity as part of GMP standards for pharmaceutical manufacturing.