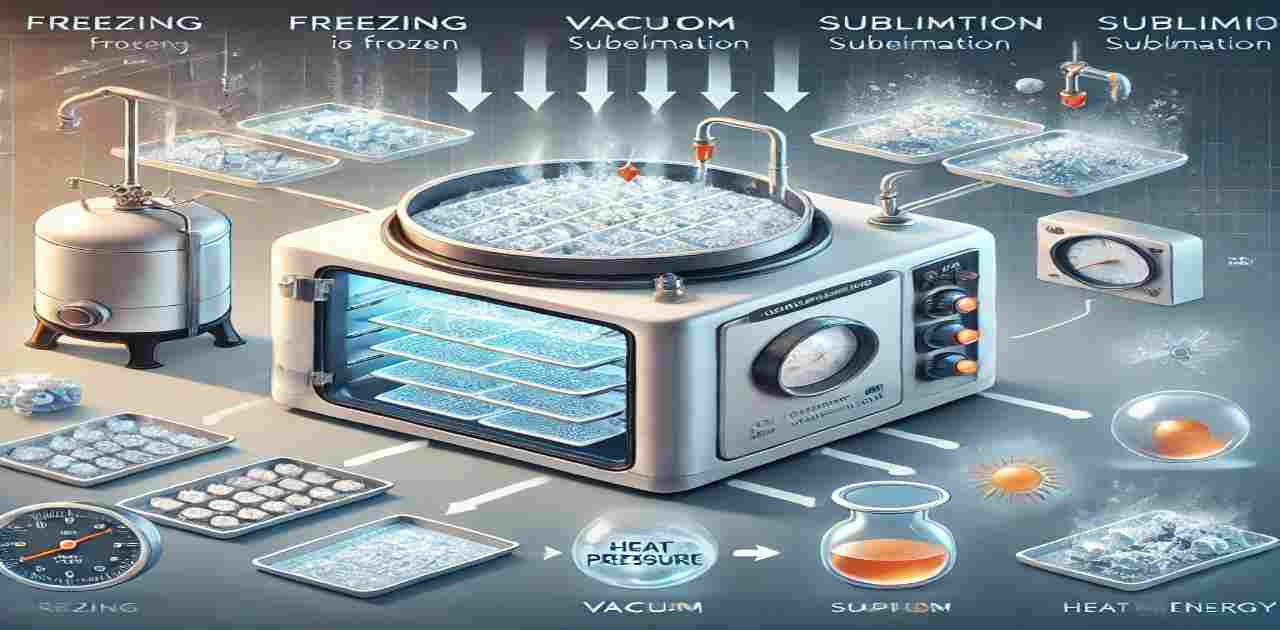
Sublimation Process in Lyophilization, Sublimation is a critical phase in the lyophilization process where a solid (ice) transitions directly into a vapor without passing through the liquid phase. This fundamental concept is pivotal to understanding freeze drying and its applications in pharmaceuticals and beyond.
Sublimation is particularly advantageous because it eliminates the need for a liquid phase, which could compromise the stability and composition of sensitive products. The process is especially critical in preserving pharmaceuticals, such as lyophilized injections, which require long shelf life and rapid reconstitution.
The sublimation process not only ensures the removal of moisture but also maintains the physical and chemical integrity of the material, making it an indispensable method for high-quality preservation.
The Sublimation Process in Freeze-Drying
Sublimation involves a phase change that requires the addition of heat energy to the frozen product. Here’s how it works in the freeze-drying process:
- Freeze: The product is entirely frozen, typically in a vial, flask, or tray.
- Vacuum: A deep vacuum is applied, lowering the pressure below the triple point of water.
- Dry: Heat energy is carefully introduced, causing the ice to sublime directly into vapor.
Importance of Sublimation in Lyophilization
In modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, lyophilized injection dosage forms have gained popularity due to their enhanced bioavailability, stability, and patient compliance. These injections are particularly beneficial for bedridden patients, offering a viable alternative to oral solid dosage forms.
For more insights on lyophilized product manufacturing, explore our CGMP guidelines for lyophilized product manufacturing.
Characteristics of Freeze-Dried Products
Successful lyophilization results in products with the following attributes:
- Strength: Ensures the product remains intact.
- Uniform color: enhances visual appeal and quality.
- Porosity: Facilitates rapid reconstitution.
- Sterility: Free from pyrogens and contaminants.
- Stability: Ensures a long shelf life in both dry and reconstituted stages.
Discover how we optimize product quality in our lyophilization cycle development guide.
Sublimation in frozen food
Sublimation in frozen food refers to the process where ice within the food directly converts into water vapor without passing through the liquid phase. This process is a key principle in freeze-drying (lyophilization), which is widely used to preserve food while maintaining its nutritional value, texture, and flavor.
How Sublimation Occurs in Frozen Food
-
Freezing
- The food is first frozen at very low temperatures (typically below -40°C).
- This ensures that water in the food forms solid ice crystals.
-
- The frozen food is placed in a vacuum chamber.
- Pressure is reduced, and heat is applied at controlled levels.
- The ice in the food sublimates, turning directly into vapor and leaving behind a porous structure.
-
Secondary Drying (Desorption)
- Residual moisture is removed by slightly increasing the temperature.
- This step ensures long-term stability and prevents microbial growth.
Factors Affecting Sublimation in Frozen Food
- Temperature: The lower the temperature, the slower the sublimation process. A precise balance is needed to prevent overheating.
- Pressure: Lowering pressure facilitates sublimation by reducing the boiling point of ice.
- Surface Area: A greater surface area speeds up sublimation.
- Vacuum Level: Stronger vacuum levels enhance sublimation efficiency.
Applications of Sublimation in Frozen Food
- Preserving fruits, vegetables, and meats
- Making instant coffee and ready-to-eat meals
- Prolonging shelf life while maintaining food quality
Parenteral Drug Administration
Parenteral routes deliver drugs directly into the bloodstream, offering 100% bioavailability. This method is ideal for potent drugs requiring precise dosing.
Advantages of Parental Administration
- Rapid onset of action.
- Suitable for unconscious or uncooperative patients.
- Avoids gastrointestinal degradation and first-pass metabolism.
Challenges
- Requires skilled administration.
- May cause pain and discomfort.
- Relatively expensive compared to oral forms.
For troubleshooting and enhancing parenteral manufacturing processes, check out our lyophilizer cleaning validation guide.
The Role of Lyophilization in Parenteral Drugs
Lyophilization ensures the stability of parenteral drugs by removing moisture and creating sterile, highly porous solids. This process is particularly vital for pharmaceuticals sensitive to aqueous instability. For tips on managing freeze-drying issues, visit our freeze dryer troubleshooting guide.
Learn More
Explore these resources to dive deeper into the freeze-drying process and related topics:
- Freeze Drying Capacity Calculator
- Cryoprotectants in Freeze-Drying: A Complete Guide
- Compressor Excess Pressure: Causes and Solutions
For a complete overview of lyophilization best practices, explore our lyophilization validation best practices.
Summary
The lyophilization process, also known as freeze-drying, is a critical preservation technique widely used in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and other industries. It relies on sublimation, a phase transition where ice directly converts to vapor without entering the liquid phase. The process comprises three primary steps: freezing, primary drying, and secondary drying, ensuring the stability and integrity of sensitive materials.
Sublimation plays a central role, especially in food processing, where it preserves the nutrients, texture, and flavor of products. Lyophilized injections, a specialized application of lyophilization, offer superior bioavailability, stability, and extended shelf life for parenteral drugs, making them ideal for therapeutic use.
Conclusion
Lyophilization is a sophisticated yet highly efficient process that leverages sublimation to achieve unparalleled preservation quality. By understanding the principles of sublimation and its application across various fields, industries can ensure product integrity, enhance stability, and meet critical therapeutic and nutritional requirements. As a result, lyophilization continues to be a cornerstone of modern preservation techniques.
FAQs
1) Sublimation Process in Lyophilization
Sublimation in lyophilization refers to the process where ice transitions directly from a solid phase to a vapor phase without passing through the liquid phase. This phase change occurs under reduced pressure and controlled temperature. It is a critical step in freeze-drying, where frozen water in the product is removed via sublimation, preserving the structure, stability, and composition of the ma
What is Lyophilized Injection?
Lyophilized injection refers to a parenteral dosage form created through lyophilization. This process stabilizes the drug by removing water, ensuring longer shelf life and easier storage. Before administration, the lyophilized powder is reconstituted with a sterile solvent to form a liquid injection. It is particularly beneficial for unstable compounds and offers high bioavailability, making it suitable for critical therapeutic applications.
Does freeze-drying use sublimation?
Yes, freeze-drying relies on sublimation as its core mechanism. During the primary drying phase, ice crystals formed during freezing are converted directly to vapor under vacuum conditions without transitioning through the liquid phase. This prevents structural damage and retains the product’s physical and chemical integrity.
What is the Process of Sublimation in Food Processing?
In food processing, sublimation occurs during freeze-drying to remove moisture from food while preserving its nutrients, flavor, and texture. The steps include:
- Freezing the food to form solid ice.
- Applying a vacuum to lower the pressure.
- Supplying heat to facilitate the sublimation of ice directly into vapor.
This method produces lightweight, shelf-stable foods commonly used in camping, emergency rations, and space missions.